Choose all statements that accurately describe the transcription bubble, a pivotal structure in the transcription process. This article delves into the intricacies of the transcription bubble, exploring its purpose, dynamics, function, regulation, and visualization techniques. By examining these key statements, we gain a comprehensive understanding of this essential molecular machinery.
The transcription bubble, a transient structure formed during transcription, plays a crucial role in facilitating the synthesis of RNA molecules. Its formation, dynamics, and regulation are tightly controlled to ensure accurate and efficient gene expression.
Transcription Bubble Overview: Choose All Statements That Accurately Describe The Transcription Bubble
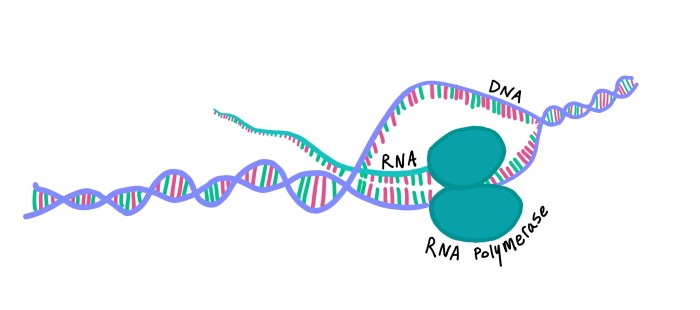
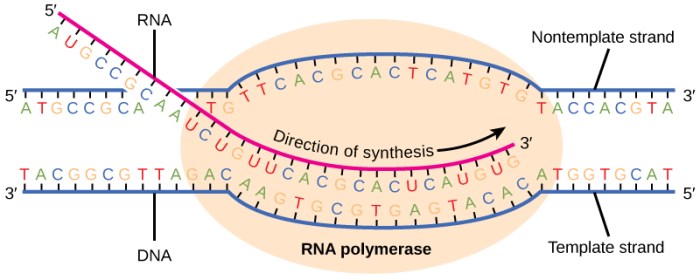
The transcription bubble is a dynamic structure that forms during gene transcription. It is a transient, localized region of DNA unwinding that allows access to the genetic code for transcription by RNA polymerase. The transcription bubble is essential for accurate and efficient gene expression.
The transcription bubble typically spans around 10-20 base pairs of DNA and is located at the transcription start site. It has a distinct appearance under electron microscopy, resembling a small, bubble-like structure at the site of transcription.
Transcription Bubble Dynamics
The size and shape of the transcription bubble are influenced by several factors, including the length of the transcribed region, the sequence of the DNA, and the binding of transcription factors.
RNA polymerase, the enzyme responsible for transcription, plays a crucial role in bubble formation. It unwinds the DNA double helix and stabilizes the transcription bubble through its interactions with the DNA and transcription factors.
Transcription Bubble Function
The transcription bubble facilitates the transcription process by providing access to the DNA template for RNA polymerase. It allows the enzyme to read the genetic code and synthesize a complementary RNA molecule.
Within the transcription bubble, RNA polymerase interacts with the DNA template strand, using it as a guide to add complementary nucleotides to the growing RNA chain.
Transcription Bubble Regulation
The formation and disassembly of the transcription bubble are tightly regulated to ensure accurate and efficient transcription.
Several proteins and factors, including transcription factors, chromatin remodelers, and termination factors, play roles in regulating bubble dynamics.
Transcription Bubble Visualization
The transcription bubble can be visualized using various techniques, including electron microscopy and biochemical assays.
Electron microscopy allows direct observation of the transcription bubble as a small, bubble-like structure at the site of transcription.
Transcription Bubble Comparison, Choose all statements that accurately describe the transcription bubble
The transcription bubble is similar to other nuclear structures involved in transcription, such as the pre-initiation complex and the elongation complex.
However, it is distinct in its transient nature and its specific role in unwinding the DNA double helix and providing access to the genetic code for RNA polymerase.
FAQ Guide
What is the primary function of the transcription bubble?
The transcription bubble facilitates the unwinding of the DNA double helix, providing access to the template strand for RNA polymerase to transcribe the genetic information into RNA molecules.
How is the size and shape of the transcription bubble determined?
The size and shape of the transcription bubble are influenced by factors such as the length of the DNA sequence being transcribed, the strength of the DNA-protein interactions, and the presence of regulatory elements.