Delving into the Periodic Table of Elements Trivia, we embark on an enthralling expedition into the realm of chemistry. This enigmatic table, a testament to scientific brilliance, holds a wealth of captivating facts and insights, unraveling the secrets of the elements that shape our world.
From the discovery of the first elements to the meticulous organization of their properties, the periodic table has revolutionized our understanding of matter. Join us as we explore the fascinating stories behind these elements, their unique characteristics, and their profound impact on various scientific disciplines.
Introduction
The periodic table of elements is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. It is widely recognized as one of the most important and fundamental organizing principles in chemistry.
The periodic table serves as a valuable tool for predicting the properties of elements and their behavior in chemical reactions. It provides insights into the electronic structure, reactivity, and bonding characteristics of elements, enabling chemists to make informed predictions and develop new materials and technologies.
The discovery and development of the periodic table is a fascinating story that spans over a century. It began with the early attempts of scientists to classify elements based on their similarities and differences, and culminated in the work of Dmitri Mendeleev, who published the first widely accepted periodic table in 1869.
Elements and Their Properties: Periodic Table Of Elements Trivia

The periodic table organizes elements into 18 vertical columns, known as groups, and 7 horizontal rows, known as periods. Each element is assigned a unique atomic number, which represents the number of protons in its nucleus. The atomic number also determines the element’s position in the periodic table.
| Atomic Number | Symbol | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | Hydrogen |
| 2 | He | Helium |
| 3 | Li | Lithium |
| 4 | Be | Beryllium |
| 5 | B | Boron |
Across the periodic table, there are general trends in atomic radius, electronegativity, and ionization energy. Atomic radius decreases from left to right across a period, while electronegativity and ionization energy increase from left to right.
The position of an element in the periodic table provides valuable information about its chemical properties. Elements in the same group tend to have similar chemical properties due to their shared valence electron configurations. Similarly, elements in the same period tend to have similar physical properties, such as atomic radius and ionization energy.
Groups and Periods
The periodic table is divided into groups and periods based on the arrangement of elements according to their atomic numbers and electron configurations.
Groups, Periodic table of elements trivia
The vertical columns in the periodic table are known as groups. Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom.
The groups are numbered 1-18 from left to right.
For example, Group 1 elements are known as alkali metals, Group 17 elements are known as halogens, and Group 18 elements are known as noble gases.
Periods
The horizontal rows in the periodic table are known as periods. Elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells. The periods are numbered 1-7 from top to bottom.
For example, Period 1 contains the elements hydrogen and helium, which have one and two electron shells, respectively. Period 7 contains the heaviest elements, such as uranium and plutonium, which have seven electron shells.
Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids
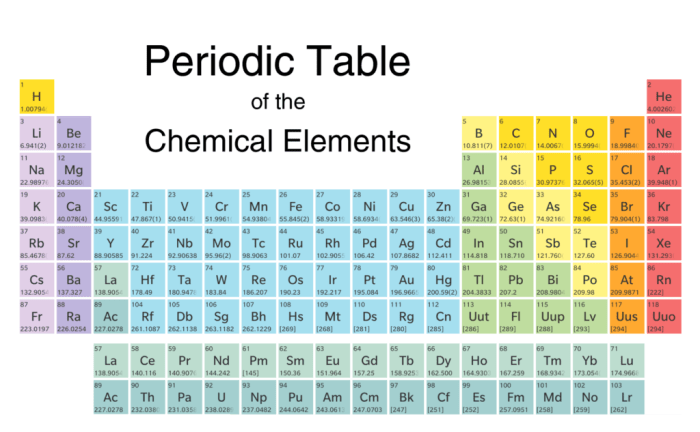
Elements can be classified into three main categories based on their properties: metals, nonmetals, and metalloids.
Metals
Metals are characterized by their shiny appearance, high electrical and thermal conductivity, and malleability and ductility. They are typically found on the left side of the periodic table.
Examples of metals include iron, copper, aluminum, and gold.
Nonmetals
Nonmetals are characterized by their dull appearance, low electrical and thermal conductivity, and brittleness. They are typically found on the right side of the periodic table.
Examples of nonmetals include oxygen, nitrogen, chlorine, and carbon.
Metalloids
Metalloids have properties that are intermediate between metals and nonmetals. They are typically found along the diagonal line running from boron to polonium on the periodic table.
Examples of metalloids include silicon, germanium, and arsenic.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the periodic table in chemistry?
The periodic table provides a systematic organization of elements based on their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemical properties. It enables scientists to predict the behavior of elements and their interactions with each other, facilitating the understanding and development of new materials and technologies.
How were the elements first discovered?
The earliest elements were discovered through alchemy, the precursor to modern chemistry. Alchemists experimented with various substances, seeking to transform base metals into gold. Over time, they isolated and identified new elements, such as gold, silver, copper, and iron.
What is the relationship between an element’s position in the periodic table and its chemical properties?
The periodic table is organized such that elements with similar chemical properties are grouped together. Elements in the same group (vertical column) share similar electron configurations, resulting in comparable chemical behavior. Elements in the same period (horizontal row) have the same number of electron shells, influencing their atomic size and ionization energy.