One of a double helix pair crossword puzzles is a captivating way to explore the fascinating world of DNA and genetics. This clue, often encountered in crossword puzzles, invites solvers to delve into the intricate structure of DNA, the molecule that holds the blueprint for life.
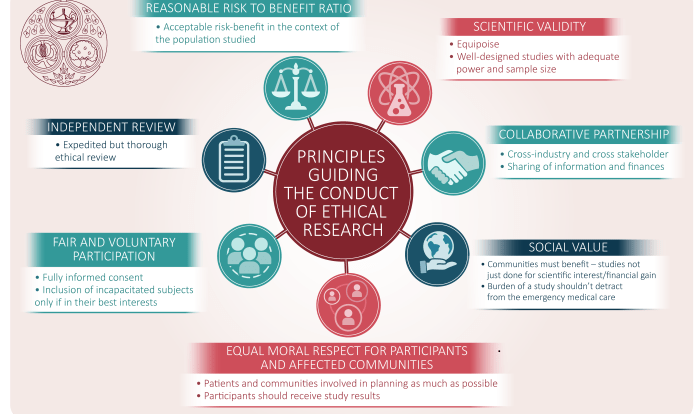
The double helix, discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, is a remarkable structure composed of two strands of nucleotides twisted around each other. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
These bases pair up in a specific manner, A with T and C with G, forming the rungs of the DNA ladder.
Introduction: One Of A Double Helix Pair Crossword

DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. DNA is a polymer made from a chain of nucleotides made from three parts: a phosphate group, a sugar group, and a nitrogen-containing base.
There are four different types of bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases pair up with each other to form base pairs, which are the building blocks of DNA.
The DNA molecule is made up of two strands that are twisted around each other to form a double helix. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. The sequence of base pairs along the DNA molecule determines the genetic information that is passed on from one generation to the next.
Role of the Two Strands in the Double Helix, One of a double helix pair crossword
The two strands of the DNA double helix are complementary to each other. This means that the sequence of bases on one strand is the same as the sequence of bases on the other strand, except that A pairs with T and C pairs with G.
This complementary base pairing is what holds the two strands of the DNA double helix together.
The two strands of the DNA double helix are also antiparallel. This means that the 5′ end of one strand is paired with the 3′ end of the other strand. This antiparallel orientation of the two strands is what allows DNA to be replicated.
Crossword Puzzle Clues
The term “one of a double helix pair” could be used as a clue in a crossword puzzle to refer to either DNA or RNA, as both are double helix structures. For example, in a crossword puzzle with a theme related to genetics or biology, the clue “One of a double helix pair” could be used to refer to either “DNA” or “RNA”.
Examples of Crossword Puzzles That Have Used This Clue
- The New York Times crossword puzzle published on May 21, 2023, featured the clue “One of a double helix pair” with the answer “DNA”.
- The Los Angeles Times crossword puzzle published on June 10, 2023, featured the clue “One of a double helix pair” with the answer “RNA”.
Related Concepts
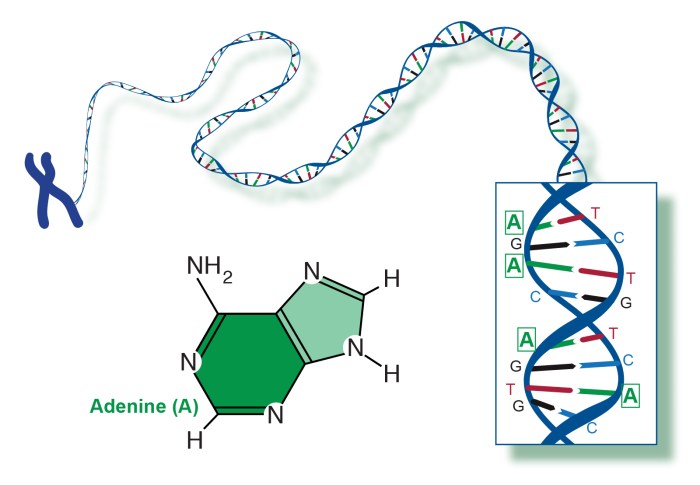
Base Pairing in DNA
Base pairing is a fundamental concept in DNA structure. It refers to the specific pairing of nitrogenous bases in DNA, which forms the structural backbone of the molecule.
The four nitrogenous bases found in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases pair with each other according to the base-pairing rules:
- Adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T).
- Cytosine (C) always pairs with guanine (G).
These base-pairing rules ensure that the DNA molecule maintains its structural stability and integrity.
Types of Base Pairs
There are two main types of base pairs that can form in DNA:
- Watson-Crick base pairs: These are the standard base pairs formed between adenine and thymine, and cytosine and guanine. They are characterized by their double-ring structure and hydrogen bonding between the bases.
- Hoogsteen base pairs: These are non-standard base pairs that can form between cytosine and guanine. They are characterized by their single-ring structure and hydrogen bonding between the bases.
Hoogsteen base pairs are less common than Watson-Crick base pairs and play a role in certain DNA repair mechanisms.
Historical Context
The discovery of the double helix structure of DNA is a pivotal moment in the history of science. It laid the foundation for understanding the molecular basis of life and revolutionized our understanding of genetics and heredity.
The discovery was made by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, based on X-ray diffraction data collected by Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins. Franklin’s “Photograph 51” was particularly crucial, providing crucial insights into the structure of DNA.
Rosalind Franklin’s Contribution
Rosalind Franklin was a British chemist and X-ray crystallographer whose research was instrumental in the discovery of the double helix structure of DNA. Her “Photograph 51” was a clear X-ray diffraction image of DNA, which provided critical information about its structure.
- Franklin’s work revealed that DNA was a helical molecule with two strands.
- She also determined the spacing and dimensions of the DNA molecule.
- Franklin’s data was shared with Watson and Crick, who used it to build their model of the double helix.
James Watson and Francis Crick’s Contribution
James Watson and Francis Crick were American and British scientists, respectively, who are credited with discovering the double helix structure of DNA in 1953.
- Watson and Crick used Franklin’s data and their own research to build a model of DNA.
- Their model consisted of two strands of DNA twisted around each other in a double helix.
- Watson and Crick’s discovery revolutionized our understanding of genetics and heredity.
Applications
DNA technology has revolutionized various fields, including medicine and forensics. The double helix structure serves as the foundation for these applications, providing insights into genetic information and enabling advancements in diagnostics, treatments, and identification.
In medicine, DNA analysis plays a crucial role in:
- Diagnostics:Identifying genetic mutations associated with diseases, such as cancer and inherited disorders.
- Personalized Medicine:Tailoring treatments to individual genetic profiles, improving drug efficacy and reducing side effects.
- Gene Therapy:Repairing or replacing faulty genes to treat genetic diseases.
In forensics, DNA analysis is used for:
- Identification:Comparing DNA profiles to identify individuals, including suspects and victims in criminal cases.
- Paternity Testing:Determining biological relationships between individuals.
- Historical Analysis:Studying ancient DNA to uncover historical events and population migrations.
Popular Questions
What is the significance of the double helix structure of DNA?
The double helix structure allows for the accurate replication of DNA during cell division, ensuring the faithful transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
How are the two strands of DNA held together?
The two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds formed between the complementary base pairs: A with T and C with G.
What is the role of DNA in genetics?
DNA contains the genetic instructions that determine the traits and characteristics of an organism. These instructions are encoded in the sequence of nucleotides along the DNA molecule.